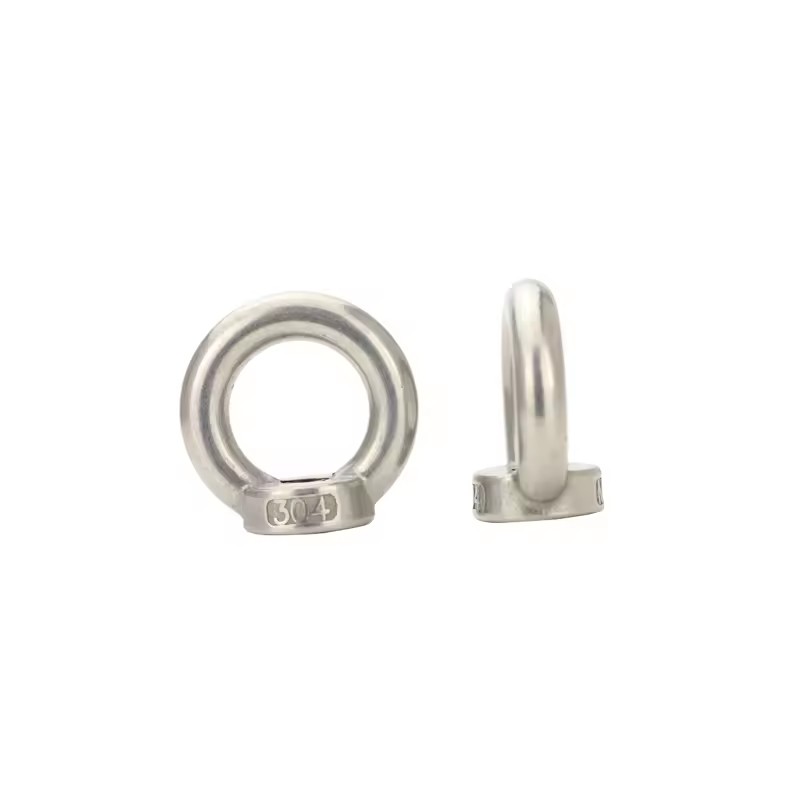
Stainless steel eye nuts are indispensable components in many industrial, construction, and marine applications. Their primary function is to serve as secure anchor points for lifting, rigging, or fastening. While most users focus on load capacity or corrosion resistance, one critical factor often overlooked is how these components perform under extreme temperature conditions.
Understanding Stainless Steel Eye Nuts
Before delving into temperature-specific considerations, it’s important to understand what stainless steel eye nuts are and why they are used.
A stainless steel eye nut is a fastening device featuring a threaded hole and a circular eye, which allows ropes, cables, hooks, or shackles to be attached. Unlike ordinary nuts, the circular eye can bear significant tension along multiple axes. They are commonly made from stainless steel grades such as 304, 316, and 321, each offering different levels of corrosion resistance and mechanical performance.
The properties that make stainless steel eye nuts popular—corrosion resistance, strength, and durability—also influence their temperature tolerance. Understanding these properties is the first step in determining their suitability for extreme conditions.
Temperature Ranges for Stainless Steel Eye Nuts
High Temperatures
Stainless steel generally maintains good strength at elevated temperatures, but the exact tolerance depends on the grade and treatment:
- Grade 304: Suitable for continuous use up to ~870°C (1600°F), but strength decreases gradually above 425°C (800°F).
- Grade 316: Offers similar temperature resistance to 304 but performs better in chemically aggressive environments.
- Grade 321: Stabilized for high-temperature applications, recommended for continuous use around 870–925°C (1600–1700°F).
Above these ranges, stainless steel eye nuts may experience oxidation, scaling, or stress relaxation, reducing load-bearing capacity. In practical terms, this means that while eye nuts may visually appear intact, their ability to safely handle heavy loads could be compromised.
Low Temperatures
At extremely low temperatures, stainless steel exhibits improved strength but reduced ductility. Most austenitic stainless steels, including 304 and 316, remain tough even down to cryogenic temperatures (-196°C / -321°F). However, non-austenitic grades may become brittle, increasing the risk of fracture under sudden load or impact.
Effects of Extreme Temperatures on Eye Nut Performance
Mechanical Strength
Temperature changes affect the tensile and yield strength of stainless steel eye nuts:
- High temperatures: The steel softens slightly, decreasing its tensile strength. Prolonged exposure can lead to creep, where the material slowly deforms under a constant load.
- Low temperatures: While tensile strength may increase, brittleness may lead to sudden fractures if the eye nut experiences impact or misaligned loads.
For critical lifting applications, these changes must be factored into working load limits. Manufacturers often provide derating charts showing maximum safe loads at elevated temperatures.
Corrosion Resistance
Extreme temperatures can also influence corrosion behavior:
- High heat: Can accelerate oxidation, especially if the environment contains oxygen or moisture.
- Low temperatures: May not directly cause corrosion, but condensation or frost formation can promote localized rust if the stainless steel grade is insufficient for the environment.
316 stainless steel is usually preferred for high-temperature marine or chemical applications because of its superior resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Thread Integrity
The threaded portion of the eye nut is critical for safe operation. Temperature fluctuations can:
- Cause thermal expansion and contraction, which may loosen the nut or create micro-gaps between threads.
- Lead to galling, especially if mating bolts are stainless steel as well, when exposed to high temperatures and insufficient lubrication.
Proper installation with compatible hardware and thread lubrication can mitigate these risks.

Practical Considerations for Using Eye Nuts in Extreme Temperatures
Selection of Material Grade
Choosing the right stainless steel grade is vital:
- 304: Adequate for moderate temperatures and general applications.
- 316: Ideal for high-temperature, marine, and chemically aggressive environments.
- 321: Best for prolonged high-temperature operations due to titanium stabilization.
When selecting, consider both maximum temperature and exposure duration, as short-term spikes are generally less damaging than sustained heat.
Installation Best Practices
Correct installation ensures reliability even under temperature extremes:
- Torque specifications: Use manufacturer-recommended torque values; over-tightening can exacerbate thermal stress.
- Thread lubrication: Reduces galling and accommodates thermal expansion.
- Orientation: For lifting applications, align the eye nut along the expected load path to minimize bending stresses.
Regular Inspection
Temperature extremes accelerate wear and tear, so regular inspections are essential:
- High-temperature applications: Check for discoloration, scaling, or deformation.
- Low-temperature applications: Look for micro-cracks or brittle fractures.
- Thread integrity: Ensure nuts remain tight and un-galled.
Documentation of inspection intervals and results is a good safety practice in industrial settings.
Real-World Applications
Stainless steel eye nuts are widely used in industries where extreme temperatures are common:
- Marine and offshore: Eye nuts made from 316 stainless steel handle both the heat from sun exposure and the cold of ocean spray.
- Foundries and steel mills: Eye nuts are exposed to molten metal heat; grade 321 is often preferred.
- Cryogenic storage: Eye nuts for liquid nitrogen tanks use austenitic stainless steel to prevent brittleness.
- Aerospace and chemical plants: Specialized eye nuts are designed to endure repeated thermal cycling without degradation.
These examples illustrate how material choice, design, and installation work together to ensure eye nuts perform safely in extreme conditions.
Summary and Recommendations
Extreme temperatures significantly influence the strength, durability, and safety of stainless steel eye nuts. Key takeaways include:
- Understand the grade: 304, 316, and 321 stainless steels each have different thermal properties.
- Account for load derating: High temperatures reduce tensile strength; low temperatures can increase brittleness.
- Ensure proper installation: Torque, lubrication, and alignment are crucial for safe use.
- Inspect regularly: Visual and mechanical checks detect early signs of failure.
- Match application to environment: High-temperature or cryogenic conditions require careful grade selection and design considerations.
By following these guidelines, engineers, riggers, and maintenance personnel can ensure that stainless steel eye nuts continue to provide reliable performance even under extreme heat or cold. Proper selection, installation, and inspection are the keys to safety and longevity.