Stainless steel machine screws are a fundamental type of fastener widely used across numerous industries. These screws are designed with external threads on a straight shank, enabling them to be inserted into a pre - tapped hole or paired with a nut to secure two or more components together. The use of stainless steel in their construction endows them with unique properties that set them apart from other types of machine screws made from different materials.
Key Characteristics of Stainless Steel Machine Screws
Corrosion Resistance
One of the most prominent features of stainless steel machine screws is their exceptional corrosion resistance. Stainless steel contains a significant amount of chromium, typically around 10.5% or more. Chromium forms a thin, invisible oxide layer on the surface of the screw when it is exposed to oxygen. This oxide layer acts as a protective barrier, preventing further oxidation and corrosion of the underlying metal. This makes stainless steel machine screws highly suitable for applications in environments where there is exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt, such as in marine, food processing, and chemical industries.
Strength and Durability
Stainless steel offers good strength properties. Different grades of stainless steel have varying levels of tensile strength. For example, 304 stainless steel, a commonly used grade, has a minimum tensile strength of around 515 MPa (74700 psi). 316 stainless steel, which contains molybdenum in addition to chromium and nickel, has even higher strength and can withstand more demanding mechanical loads. This strength, combined with its corrosion resistance, ensures that stainless steel machine screws can maintain their integrity and hold components together securely over long periods, even in harsh conditions.
Temperature Resistance
Stainless steel machine screws can withstand a wide range of temperatures. They can be used in both high - temperature and low - temperature applications. In high - temperature environments, stainless steel retains its mechanical properties better than many other materials. For instance, in industrial furnaces or exhaust systems, where temperatures can reach several hundred degrees Celsius, stainless steel machine screws can continue to function effectively without significant loss of strength or corrosion. Similarly, in cryogenic applications, such as in the storage and transportation of liquefied gases, stainless steel machine screws maintain their toughness and do not become brittle.
Aesthetic Appeal
In addition to their functional properties, stainless steel machine screws often have an attractive, shiny finish. This makes them a popular choice in applications where appearance matters, such as in architectural and decorative uses. The smooth, clean look of stainless steel screws can enhance the overall aesthetic of a product or structure, while still providing reliable fastening.
Types of Stainless Steel Machine Screws
Based on Head Styles
Pan Head: Pan - head machine screws have a rounded, dome - shaped head with a flat top. This head style provides a relatively large bearing surface, which helps distribute the load evenly when the screw is tightened. Pan - head screws are commonly used in applications where a flush or semi - flush finish is desired, and they can be easily driven using a screwdriver or a power tool with the appropriate bit.
Flat Head: Flat - head machine screws have a conical - shaped head that sits flush or nearly flush with the surface when installed. They are ideal for applications where a low - profile appearance is crucial, such as in furniture making or in applications where the surface needs to be as smooth as possible to avoid interference with other components.
Oval Head: Oval - head machine screws feature a low - dome head that is tapered, which allows for counter - sinking. This means the head of the screw can be recessed into the material, creating a smooth surface. Oval - head screws are often used in applications where both a secure fastening and an aesthetically pleasing finish are required.
Hex Head: Hex - head machine screws have a six - sided head. They can be tightened using a wrench, which provides more torque compared to using a screwdriver for other head styles. Hex - head screws are commonly used in applications where a high level of torque needs to be applied, such as in machinery and automotive repairs.
Based on Drive Types
Phillips Drive: Phillips - drive machine screws have a cross - shaped slot in the head. This is one of the most common drive types in the United States. The Phillips design allows for better engagement with the screwdriver bit, reducing the likelihood of the bit slipping out during installation. However, at lower torque levels, there is a tendency for the bit to cam out, which was actually a deliberate design feature to prevent overtightening, especially in applications like assembling aluminum aircraft.
Slotted Drive: Slotted - drive machine screws have a single, straight slot in the head. They are the simplest and most basic drive type. While they are easy to use with a standard flat - bladed screwdriver, they are more prone to slipping compared to Phillips - drive screws, especially when applying high torque.
Allen (Hexagon Socket) Drive: Allen - drive machine screws have a hexagonal socket in the head. A hex - key is used to drive these screws. This drive type provides a very secure and precise fit, allowing for high - torque applications. Allen - drive screws are often used in machinery and high - precision equipment where accurate tightening is essential.
Based on Stainless Steel Grades
304 Stainless Steel: This is one of the most commonly used grades of stainless steel for machine screws. It contains approximately 18% chromium and 8% nickel, which gives it good corrosion resistance in general atmospheric conditions. 304 stainless steel machine screws are suitable for a wide range of applications, including those in the food and beverage industry, general manufacturing, and architectural applications.
316 Stainless Steel: Also known as marine - grade stainless steel, 316 contains 2 - 3% molybdenum in addition to chromium and nickel. The molybdenum content enhances its corrosion resistance, especially in harsh environments such as saltwater. 316 stainless steel machine screws are extensively used in marine applications, such as on boats and in docks, as well as in chemical processing plants where exposure to corrosive chemicals is common.
410 Stainless Steel: 410 stainless steel is a martensitic stainless steel. It has higher strength and hardness compared to austenitic stainless steels like 304 and 316. However, its corrosion resistance is somewhat lower. 410 stainless steel machine screws are often used in applications where a combination of strength and moderate corrosion resistance is required, such as in some automotive and machinery components.
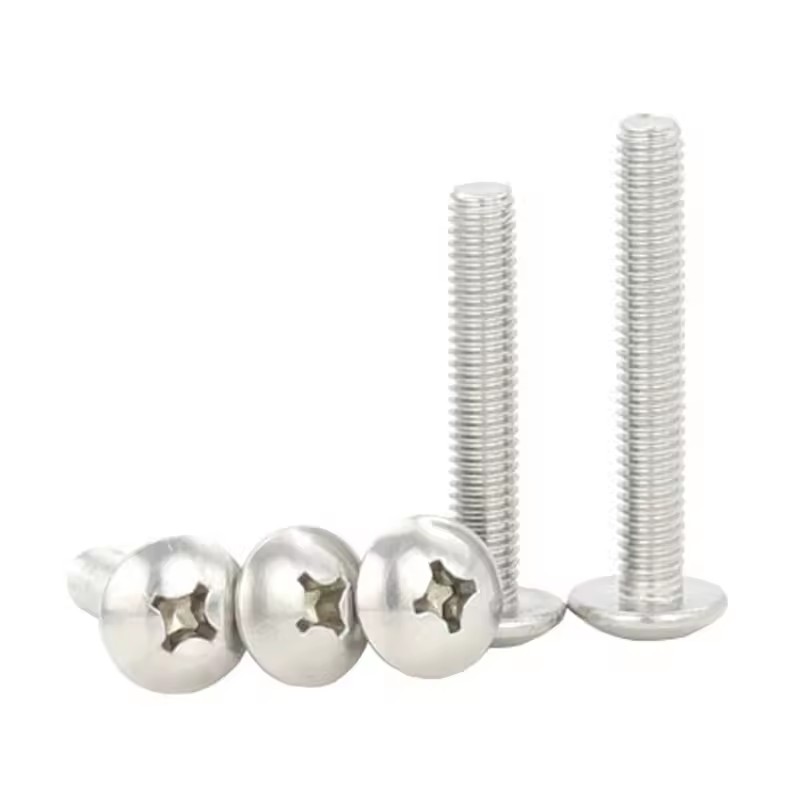

Applications of Stainless Steel Machine Screws
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, stainless steel machine screws are used in various components. They are used to fasten engine parts, where they need to withstand high temperatures, vibrations, and exposure to engine oils and coolants. Stainless steel screws are also used in the assembly of body panels, as they provide a corrosion - resistant and durable fastening solution. Additionally, in automotive interiors, stainless steel machine screws are used to secure decorative elements and components, where their aesthetic appeal is also important.
Marine Industry
The marine environment is highly corrosive due to the presence of saltwater. Stainless steel machine screws, especially those made of 316 grade, are essential in the marine industry. They are used to build and maintain boats, yachts, and other watercraft. Stainless steel screws are used to fasten hull components, deck fittings, and engine parts. Their corrosion resistance ensures that the integrity of the vessel is maintained over time, even with constant exposure to saltwater and harsh weather conditions.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, hygiene and corrosion resistance are of utmost importance. Stainless steel machine screws are used in the construction of food processing equipment, such as conveyors, mixers, and packaging machinery. The smooth surface of stainless steel makes it easy to clean and sanitize, preventing the buildup of bacteria and contaminants. Additionally, the corrosion resistance of stainless steel ensures that the screws do not corrode when exposed to food products, cleaning agents, or moisture, which could contaminate the food.
Construction and Architecture
Stainless steel machine screws are widely used in construction and architecture. In building structures, they are used to fasten metal components, such as in the construction of steel - framed buildings. Their strength and corrosion resistance make them suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications. In architectural applications, stainless steel screws are used to install decorative elements, such as handrails, facades, and signage. Their aesthetic appeal and durability enhance the overall look and functionality of the building.
Medical Industry
In the medical industry, stainless steel machine screws are used in medical devices and equipment. They are used in the construction of surgical instruments, where they need to be corrosion - resistant and able to withstand repeated sterilization processes. Stainless steel screws are also used in prosthetics and orthopedic implants. The biocompatibility of certain grades of stainless steel, such as 316L (a low - carbon version of 316), makes them suitable for use in contact with the human body.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Machine Screw
Consider the Application Environment
The first step in choosing the right stainless steel machine screw is to consider the application environment. If the screw will be used in a highly corrosive environment, such as in a marine or chemical processing setting, a higher - grade stainless steel like 316 or 316L should be selected. For general indoor applications or those with low - corrosion risk, 304 stainless steel may be sufficient. If the application involves high temperatures, the temperature resistance of the stainless steel grade should be taken into account.
Determine the Required Strength
The strength requirements of the application also play a crucial role in screw selection. For applications that require high - torque fastening or where the screw will be subjected to heavy mechanical loads, a grade of stainless steel with higher tensile strength should be chosen. For example, if the screw is used to secure a critical component in a machine, 316 stainless steel, which has higher strength compared to 304 in some cases, may be more appropriate.
Match the Head and Drive Types
The head and drive types of the machine screw should be selected based on the application requirements. If a flush or low - profile finish is needed, a flat - head or oval - head screw may be the best choice. For applications where high - torque application is required, a hex - head or Allen - drive screw should be considered. The drive type should also be compatible with the tools available for installation.
Check the Screw Size and Thread Pitch
The size of the machine screw, including its diameter and length, should be carefully chosen to fit the components being fastened. The thread pitch, which is the distance between adjacent threads, should also match the pre - tapped hole or nut. Using the wrong size or thread pitch can result in a poor fit, reduced fastening strength, and potential failure of the assembly.
Conclusion
Stainless steel machine screws are versatile and reliable fasteners that offer a combination of corrosion resistance, strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. With a wide range of types available, including different head styles, drive types, and stainless steel grades, they can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of various industries and applications. By carefully considering the application environment, strength needs, head and drive types, and screw size, the right stainless steel machine screw can be selected to ensure a secure and long - lasting fastening solution.